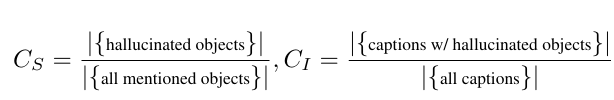(CVPR 2024)
引言 MLLMs 也面临着一个称为“幻觉”问题的重大挑战。具体而言,MLLMs 经常对用户提供的图像和提示产生不正确的声明,例如生成无关或无意义的响应,在颜色、数量和位置方面识别图像中不存在的错误物体。
各种方法 [23, 33, 34, 39]被提出以减少 MLLM 中的幻觉。
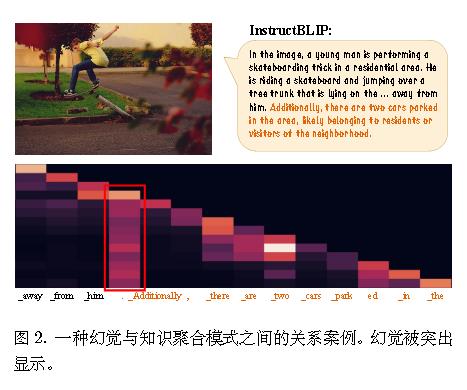
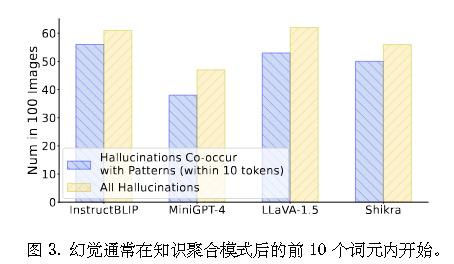
作者发现,幻觉许多幻觉内容的出现与列状注意力模式生成的后续词元相吻合。
值得注意的是,这些列状注意力模式通常出现在缺乏实质性信息的词元上,例如句号或引号。
一个表现出列状注意力模式的词元通常包含有限的信息,却对所有后续词元的预测产生显著影响,大多数后续内容包含推理或幻觉。基于上述观察,作者假设此类词元作为摘要词元,即从序列中的先前词元中聚合关键知识并指导后续词元生成。
在解码词元$x_t$时,每个候选假设将根据 Logit 中的Top-$N _ {beam}$ 概率选择 $N _ {beam}$ 个候选词元。最后,解码过程将输出获得最佳束得分的假设。
另外,基于$Logit p(x_t|x _ {<t}) $,发展了几种解码策略。OPERA 基于束搜索 (bean search),这是一种基于累积得分的解码策略。简而言之,给定一个束大小 $N _ {beam}$ ,束搜索会保留 Nbeam 个候选序列,其中每个候选序列是一个解码序列 $x^{N _ {beam}}$,带有束得分。
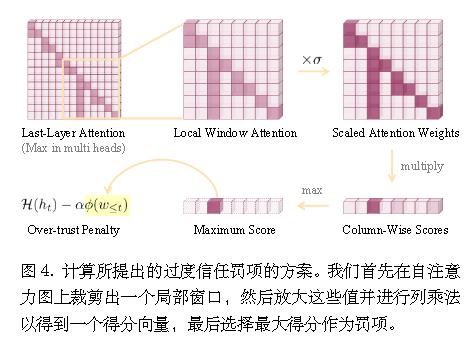
算法 过度信任 Logit 惩罚
裁剪局部窗口:
注意力缩放:
$$
对注意力矩阵的下三角部分进行列-wise 乘法运算:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 attn_pos = key_position"response_start" ]:, attn_pos["response_start" ]:]for j in range (attn_local.shape[-1 ]):1e-7 * attn_local[..., j:, j].prod(-1 ).data1 ]1 , attn_pos["image_start" ]:attn_pos["image_end" ]+1 ].sum (-1 )max (-1 )if cur_response_lens <= 10 else rollback_scores"candidate_token_scores" ] = candidate_token_scores.clone()
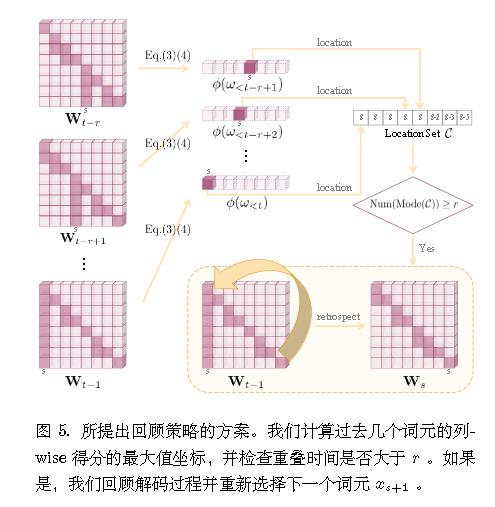
回顾-分配策略 然而,仍然存在一些情况,其中所有候选词都受到惩罚且幻觉已经发生。这是由于前几个后续词元过度信任了摘要词元,而惩罚机制未能纠正它们。因此,一个直观但激进的想法是,如果我们能排除导致幻觉的词元,并在摘要词元之后重新选择合适的前几个词元,这种模式将大大减弱。
$$
假设序列$\{x_0, x_1, . . . , x_s, . . . , x _ {t−1}\}$在 摘 要 词 元 xs 处 展 示 了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 try :if all ((rollback_loc_gather == rollback_loc).long().sum () > int (threshold) for _, rollback_loc_gather in enumerate (rollback_loc_gathers)):if rollback_loc < 10 : assert False 1 if max_rollback_time[rollback_pos] >= num_attn_candidates:1 if max_rollback_time[rollback_pos] >= num_attn_candidates:assert False else :1 else :1 if cur_response_lens - rollback_pos > history_length + 1 :max (1 , cur_response_lens - history_length - 1 )for j in range (cur_response_lens-rollback_pos-2 ):1 )1 )1 )] = []2 ]["input_ids" ]2 ]["beam_scorer" ]2 ]["beam_indices" ]2 ]["cur_len" ]2 ]["attn_previous" ].to(input_ids.device)2 ]["candidate_token_scores" ]2 ]["candidate_tokens" ]2 ]["beam_scores" ]1 ]["beam_next_tokens" ]1 ]["beam_idx" ]if "images" in model_kwargs_ori.keys():"attention_mask" ] = torch.cat(["attention_mask" ], torch.ones((0 ], input_ids[:,:-1 ].shape[1 ] - model_kwargs["attention_mask" ].shape[1 ]1 )self .prepare_inputs_for_generation(input_ids[:,:-1 ], **model_kwargs)else :self .model.embed_tokens(input_ids[:,1 :-1 ])"inputs_embeds" ] = torch.cat([model_kwargs["inputs_embeds" ], answer_embeds], 1 )"attention_mask" ] = torch.cat("attention_mask" ], torch.ones_like(input_ids[:,1 :-1 ]).to(input_ids.device)], 1 )self .prepare_inputs_for_generation(input_ids[:,1 :-1 ], **model_kwargs)self (True ,self ._update_model_kwargs_for_generation(self .config.is_encoder_decoderself .prepare_inputs_for_generation(input_ids, **model_kwargs)self (True ,1 , :]del outputs_tmp, model_inputs_tmp1 )1 )1 ] = []999. + next_token_logits.min (-1 , keepdim=True ).values.dataif len (reject_token_pos_gather[rollback_pos]) > 0 :1 )1 , reject_token_pos, -999. )else :assert False except :999. )1 , candidate_tokens, candidate_token_scores)
实验
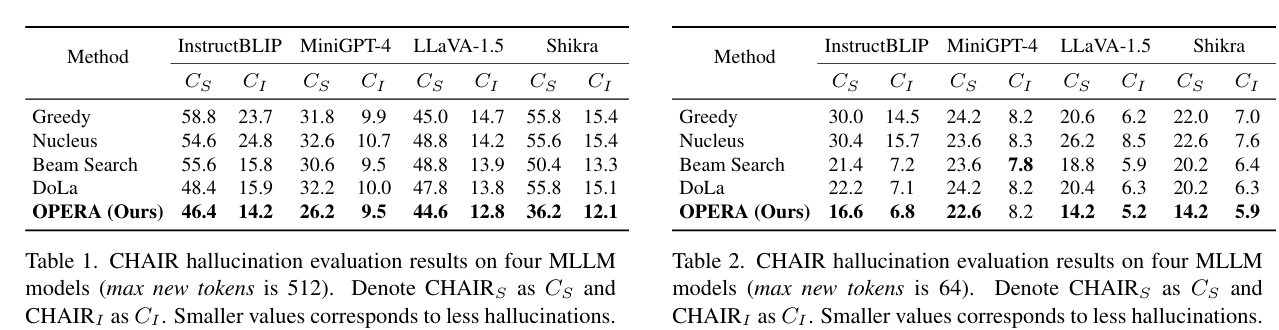
令人奇异的是,beam search的幻觉率居然比top-k、top-p相对更低。
但想想似乎也存在一定的合理性。提出top-p的《The Curious Case of Neural Text Degeneration》也说明了beam search更容易重复,而缺乏新意。
题外话 后续的还有2407.15130、2409.20429、2501.15269、2503.08342。
视觉方面也有相关研究:2503.07772