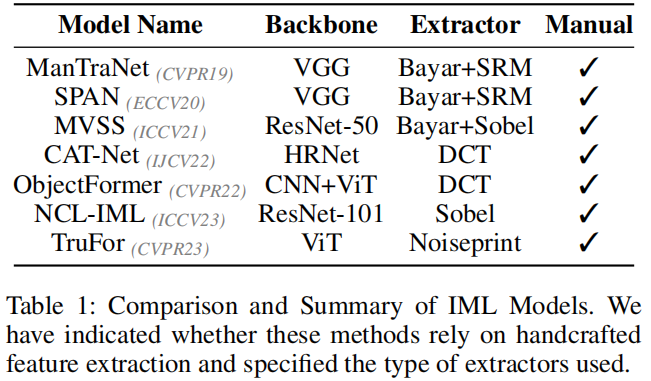
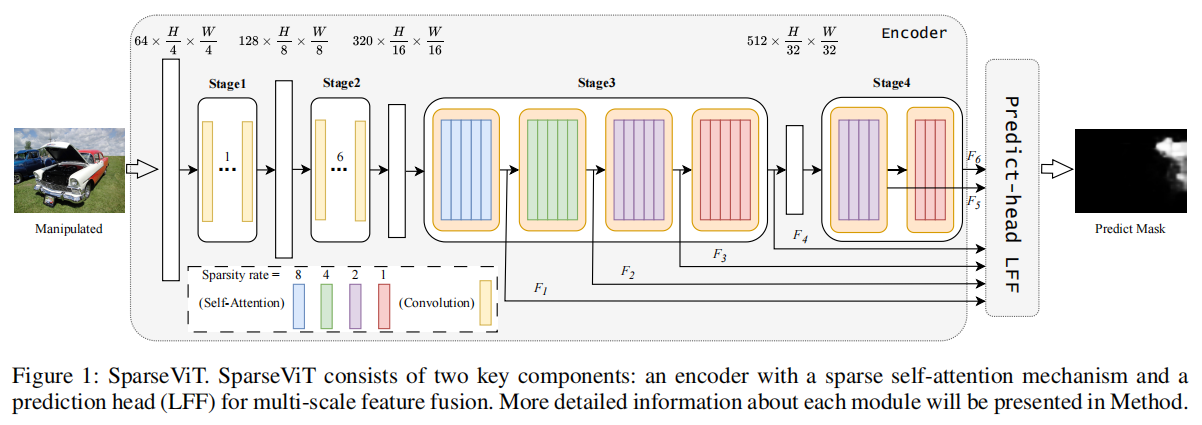
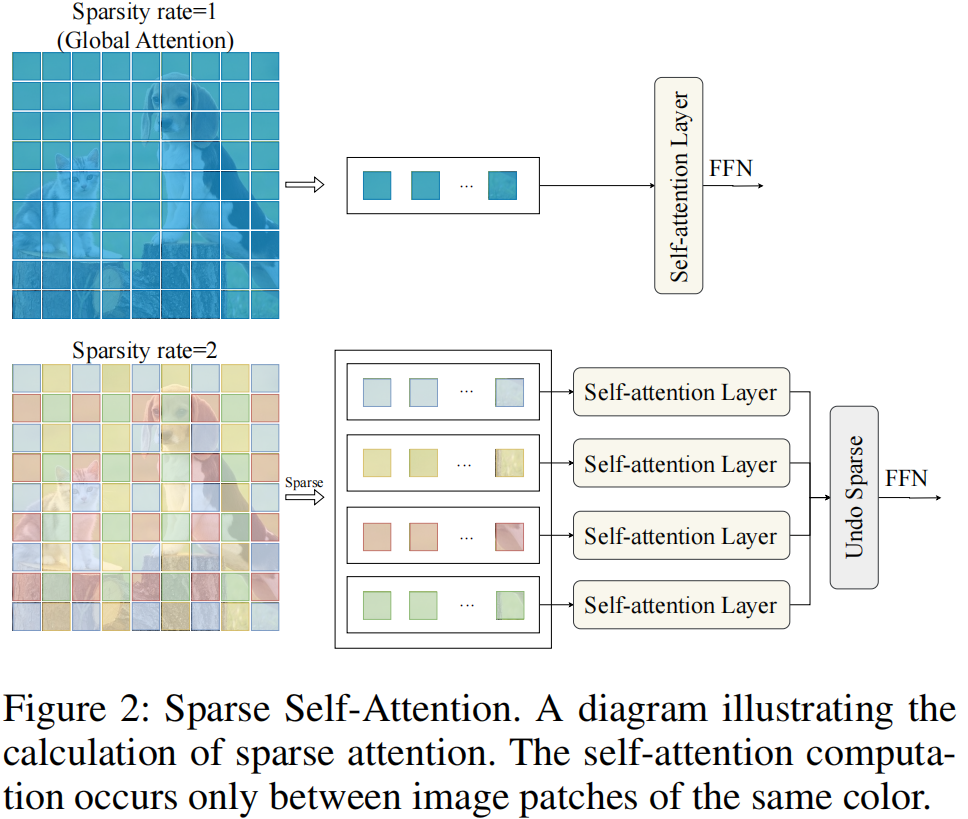
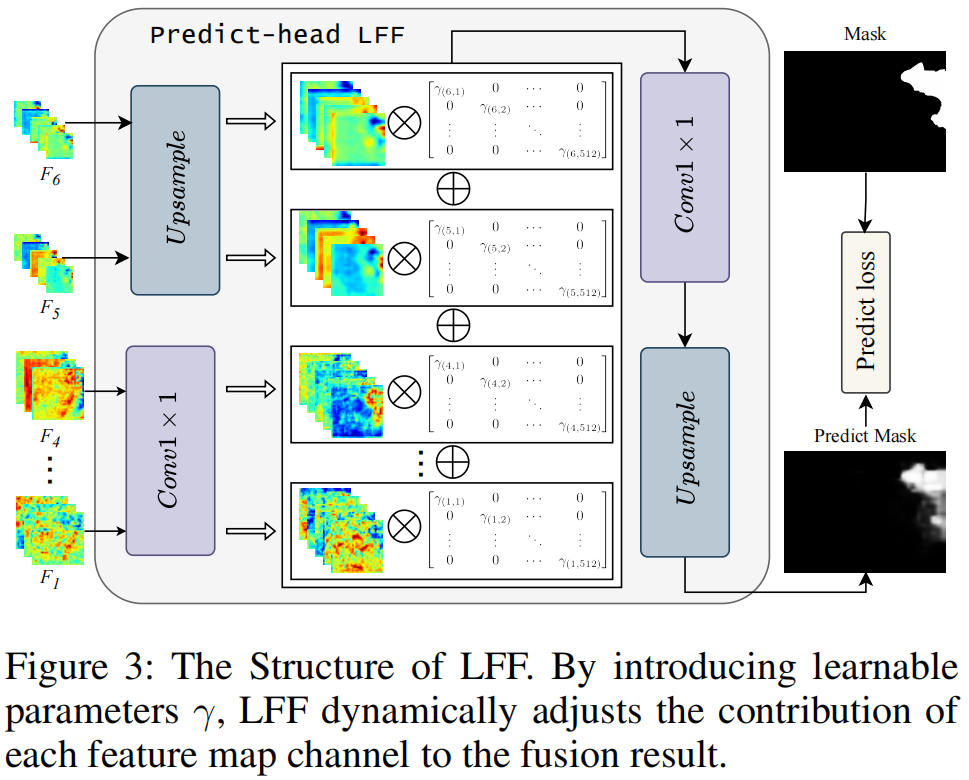
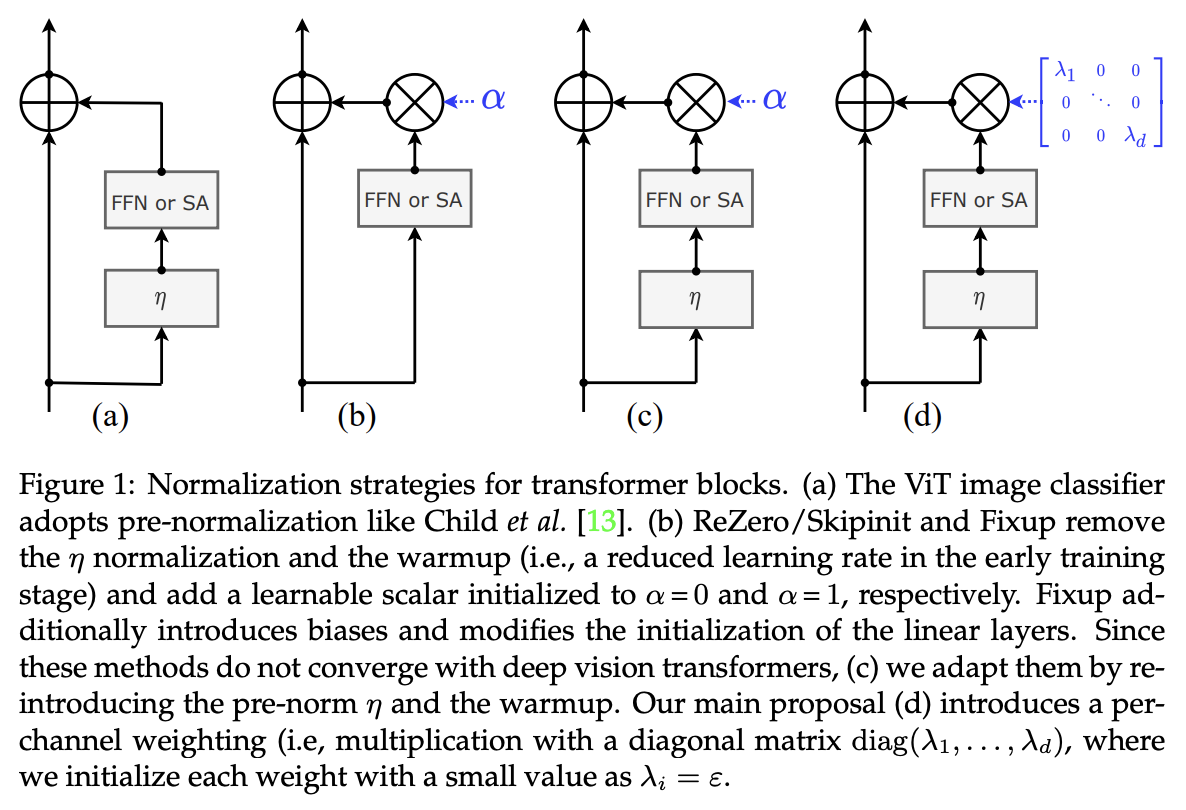
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from functools import partial
class Multiple(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
init_value = 1e-6,
embed_dim = 256,
predict_channels = 1,
norm_layer = partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=1e-6) ):
super(Multiple, self).__init__()
self.gamma1 = nn.Parameter(init_value * torch.ones((embed_dim)),requires_grad=True)
self.gamma2 = nn.Parameter(init_value * torch.ones((embed_dim)),requires_grad=True)
self.gamma3 = nn.Parameter(init_value * torch.ones((embed_dim)),requires_grad=True)
self.gamma4 = nn.Parameter(init_value * torch.ones((embed_dim)),requires_grad=True)
self.gamma5 = nn.Parameter(init_value * torch.ones((embed_dim)),requires_grad=True)
self.gamma6 = nn.Parameter(init_value * torch.ones((embed_dim)),requires_grad=True)
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
self.conv_layer1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=320, out_channels=512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv_layer2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=320, out_channels=512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv_layer3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=320, out_channels=512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv_layer4 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=320, out_channels=512, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv_last = nn.Conv2d(embed_dim, predict_channels, kernel_size= 1)
def forward(self, x):
c1, c2, c3, c4, c5, c6 = x
c1 = self.conv_layer1(c1)
c2 = self.conv_layer2(c2)
c3 = self.conv_layer3(c3)
c4 = self.conv_layer4(c4)
b, c , h, w = c1.shape
c5 = F.interpolate(c5, size=(h, w), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
c6 = F.interpolate(c6, size=(h, w), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
c1 = c1.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
c2 = c2.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
c3 = c3.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
c4 = c4.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
c5 = c5.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
c6 = c6.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
x = self.gamma1*c1 + self.gamma2*c2 + self.gamma3*c3 + self.gamma4*c4 + self.gamma5*c5 + self.gamma6*c6
x= x.transpose(1, 2).reshape(b, c, h, w)
x = (self.norm(x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1))).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous()
x = self.conv_last(x)
return x
|