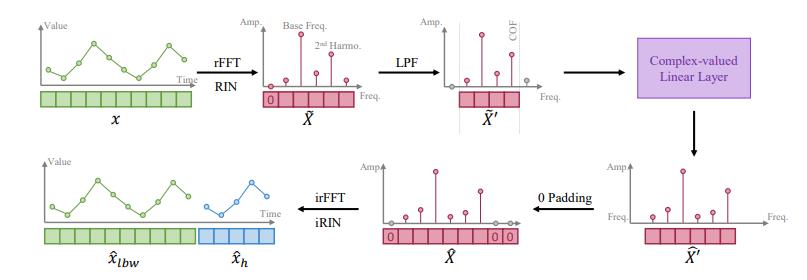
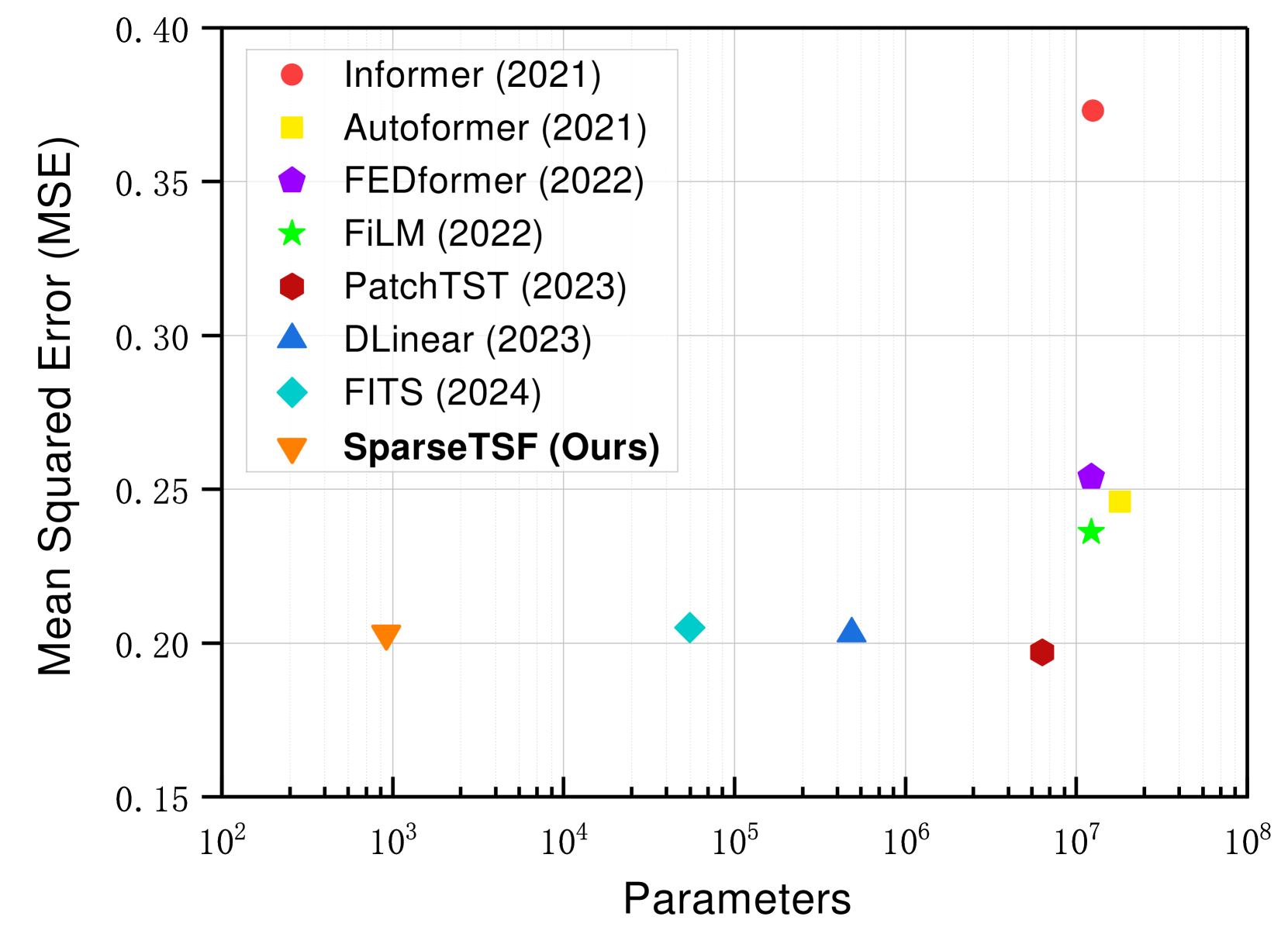
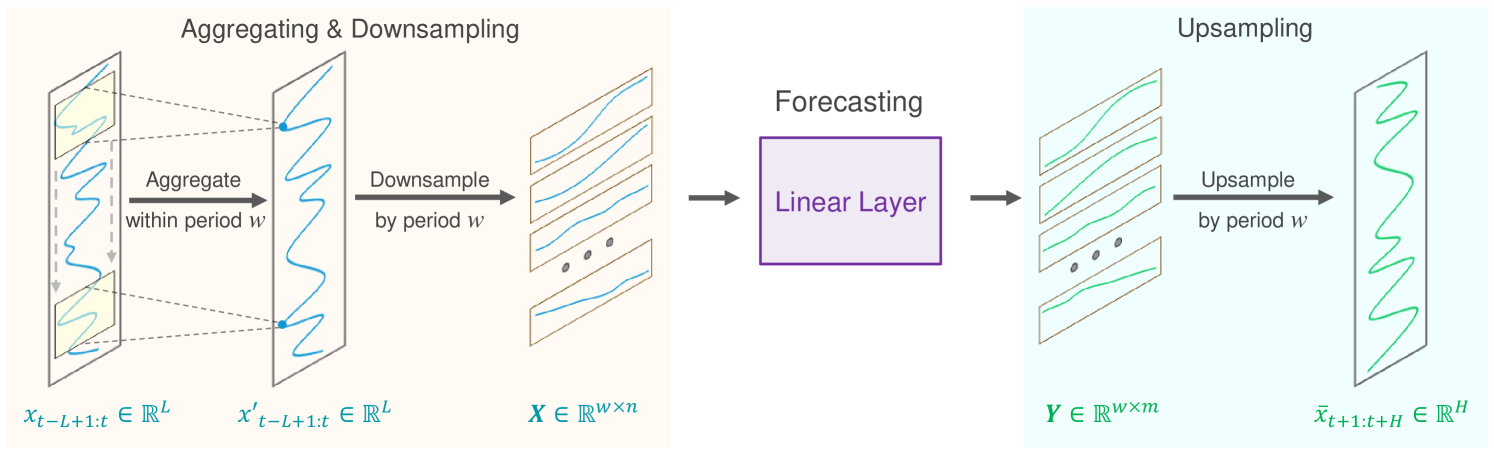
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import models.NLinear as DLinear
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, configs):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.seq_len = configs.seq_len
self.pred_len = configs.pred_len
self.individual = configs.individual
self.channels = configs.enc_in
self.dominance_freq=configs.cut_freq
self.length_ratio = (self.seq_len + self.pred_len)/self.seq_len
if self.individual:
self.freq_upsampler = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(self.channels):
self.freq_upsampler.append(nn.Linear(self.dominance_freq, int(self.dominance_freq*self.length_ratio)).to(torch.cfloat))
else:
self.freq_upsampler = nn.Linear(self.dominance_freq, int(self.dominance_freq*self.length_ratio)).to(torch.cfloat)
def forward(self, x):
x_mean = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
x = x - x_mean
x_var=torch.var(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)+ 1e-5
x = x / torch.sqrt(x_var)
low_specx = torch.fft.rfft(x, dim=1)
low_specx[:,self.dominance_freq:]=0
low_specx = low_specx[:,0:self.dominance_freq,:]
if self.individual:
low_specxy_ = torch.zeros([low_specx.size(0),int(self.dominance_freq*self.length_ratio),low_specx.size(2)],dtype=low_specx.dtype).to(low_specx.device)
for i in range(self.channels):
low_specxy_[:,:,i]=self.freq_upsampler[i](low_specx[:,:,i].permute(0,1)).permute(0,1)
else:
low_specxy_ = self.freq_upsampler(low_specx.permute(0,2,1)).permute(0,2,1)
low_specxy = torch.zeros([low_specxy_.size(0),int((self.seq_len+self.pred_len)/2+1),low_specxy_.size(2)],dtype=low_specxy_.dtype).to(low_specxy_.device)
low_specxy[:,0:low_specxy_.size(1),:]=low_specxy_
low_xy=torch.fft.irfft(low_specxy, dim=1)
low_xy=low_xy * self.length_ratio
xy=(low_xy) * torch.sqrt(x_var) +x_mean
return xy, low_xy* torch.sqrt(x_var)
|